|
 |
 |
|---|
 |
|---|
 |
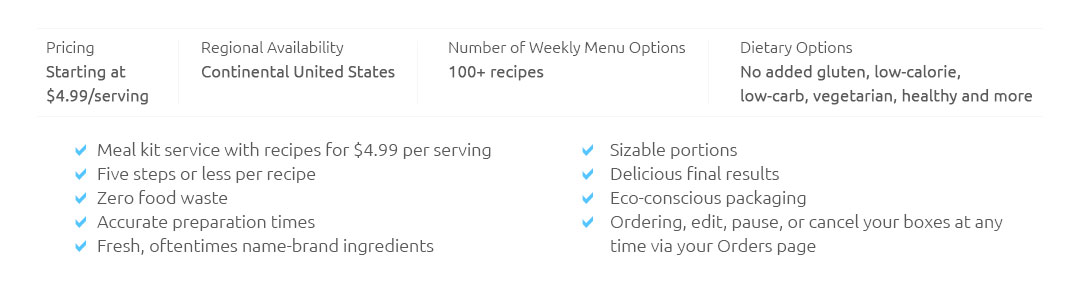
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|---|
The Evolution and Impact of Frozen Meals in Modern CuisineIn the bustling corridors of contemporary life, where time is often the most precious commodity, frozen meals have carved a niche as both a culinary savior and a subject of nutritional scrutiny. The history of these convenient meals traces back to the early 20th century, with Clarence Birdseye pioneering the flash-freezing process that revolutionized food preservation. Today, the frozen food aisle is a testament to innovation, offering a diverse array of options that cater to varied palates and dietary needs. One of the most compelling aspects of frozen meals is their ability to blend convenience with flavor. Gone are the days when these meals were synonymous with bland, uninspired fare. The industry has seen a significant transformation, driven by consumer demand for high-quality, nutritious options. Brands are increasingly focusing on organic ingredients, balanced nutrition, and diverse culinary traditions, allowing individuals to explore global flavors from the comfort of their homes. However, while the convenience factor is undeniable, it is crucial to approach frozen meals with a discerning eye. Many products, despite their appealing packaging and claims, can be high in sodium, preservatives, and unhealthy fats. Therefore, understanding how to read nutritional labels is an essential skill for consumers aiming to make healthier choices. Prioritizing meals with whole grains, lean proteins, and ample vegetables can significantly enhance their dietary value. From an environmental perspective, the frozen food industry is making strides in sustainability. Innovations in packaging technology, such as recyclable and biodegradable materials, reflect a growing awareness of the ecological footprint associated with frozen meals. Additionally, the industry's ability to reduce food waste is noteworthy. The freezing process extends the shelf life of foods, which can lead to more efficient use of resources and a reduction in household waste. In conclusion, while frozen meals offer a quick and often satisfying solution to mealtime dilemmas, they also present an opportunity for consumers to make informed, health-conscious decisions. By selecting options that prioritize nutritional quality and sustainable practices, individuals can enjoy the benefits of modern convenience without compromising on health or ethics. Ultimately, the evolution of frozen meals mirrors broader trends in food technology and consumer awareness, serving as a reflection of our changing relationship with food in the 21st century. https://www.omahasteaks.com/buy/Meals-Sides-and-Desserts/One-Step-Meals?srsltid=AfmBOoo6V4FdqjpXt1odB1UO2-RXhKef6PD8ab8QeVr63FCA5_vPmnw3
One-step frozen meals deliver a delicious, no-stress option for busy weeknight dinners. Simple to prepare and easy to enjoy, order online today! https://www.goodnes.com/stouffers/products/frozen-dinners/
80 Results - Baked Ziti - Baked Chicken - Beef and Broccoli - Beef Pot Roast - Cheddar Potato Bake - Cheese Lovers Lasagna - Cheesy Macaroni & Beef - Cheesy ... https://www.walmart.com/browse/food/frozen-meals/976759_976791_6259087
Frozen Family Meals, Frozen Family Meals, Frozen Individual Meals, Frozen Individual Meals, Frozen Health-Inspired Meals, Frozen Health Inspired Meals
|
|---|